Ad Code
Translate
Five Do’s For a Healthy Turnover That Bolsters Talent-Retention
October 20, 2025
Smart strategies for trading on crypto exchanges
October 20, 2025
What is Ozempic (semaglutide)? (Updated in 2025)
January 30, 2025
Discover Honeybee Pharmacy (2025 Guide Important Consumer Tips)
October 14, 2025
Posture Bra: Improving Back Support and Comfort
October 20, 2025
How To Find Suitable Properties In Cyprus?
October 20, 2025
10 Effective Strategies to Improve Domain Authority of Your Website
October 20, 2025
What You Need to Know About Gingivitis
Zizo Gala-Mkhize
August 18, 2022
Health is essential to human life, and severe effects are felt when good health is compromised. Ideally, the health of each part of the body is equally important. But unfortunately, most people forget the health of their teeth, tongue, and gums.
Teeth play a pivotal role in breaking down food for easy consumption and laying the ground for further digestion. Moreover, teeth maintain the structural integrity of the oral cavity and contribute to the overall aesthetics of the mouth. In addition, teeth are held firmly to the jaw with the surrounding gum tissue, which also protects the highly vulnerable parts of the teeth.
The optimal function of teeth and the surrounding structures requires good oral care—inadequate care results in disease and complications, such as gingivitis. Gingivitis is one of the most prevalent oral diseases in the world, and around 29% of the population aged fifteen and above suffer from it.
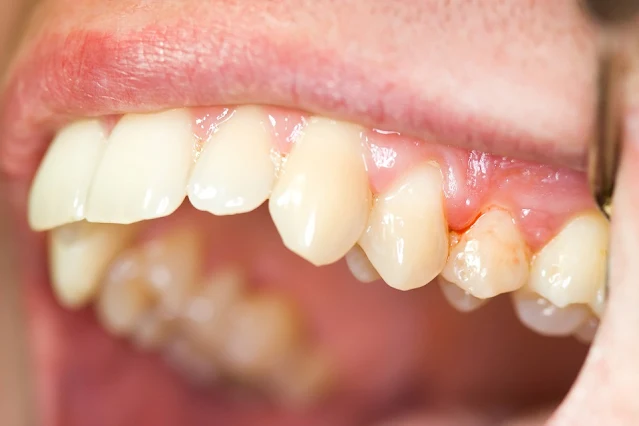
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gingiva, the part of the gum surrounding the teeth. Swelling, irritation, and bleeding of the gingiva are some of the classic signs of gingivitis. However, here is a closer look at what causes gingivitis and how you can treat it.
Causes of gingivitis
Several factors are responsible for the onset and progression of inflammation along the gingiva. These include;
Plaque buildup
Accumulating small food particles and bacteria in the mouth leads to a sticky substance that coats the gum, teeth and plaque. As the plaque builds, it undergoes impaction to form tartar and calculus. Eventually, gingivitis sets in.
Medications
Although medicines treat diseases, their side effects can cause more harm than good. Certain drugs reduce saliva production, which is instrumental in maintaining good oral health. Unfortunately, dry mouth lays the ground for bacterial spread and the onset of gingivitis.
Infections
Several infections that affect the mouth contribute to the acquisition of gingivitis. Good examples are oral thrush and oral herpes. Moreover, systemic diseases that lower immunity also increases the risk of developing gingivitis. Some of the disorders include HIV and diabetes. Fortunately, most of the conditions are manageable, if not curable.
Poor nutrition
The choice of diet is vital to the health of teeth and gums. Unfortunately, insufficient nutrients in the diet impact gum tissues, leaving them vulnerable to infections. For example, calcium, vitamin B, and vitamin C deficiency increase the risk of gingivitis.
In addition to the listed causes, hormonal change or imbalance, smoking, age, and genetics can also cause gingivitis.
Signs and symptoms
Gingivitis often presents with the classical signs of inflammation. Here are what to expect;
A change in gum colour
A healthy gum initially portrays a relatively pink colour. However, if the gums become dark, white, or dusky red, this could indicate gingivitis.
Bleeding gums
Normal gums don't bleed. Therefore, you may have gingivitis if you notice bleeding after brushing your teeth or flossing. Moreover, the inflammation is likely severe if bleeding occurs without insult.
Other symptoms include swelling in the gums, bad breath, and tenderness.
How to prevent gingivitis
Prevention is better than cure, especially for gingivitis. Self-discipline and proper oral hygiene is the game changer in gum inflammation. In addition, prevention will save you the embarrassment of enduring the complications of gingivitis and undertaking surgical procedures to remedy the problem. Therefore, here is what you can do to avoid gingivitis;
Visit your dentist regularly.
Professional check-ups conducted by dentists are your greatest weapon against gingivitis. Dentists perform several preventative services, including cleaning teeth to prevent the unnecessary accumulation of bacteria and tartar. Moreover, early diagnosis results in early intervention, guaranteeing a good outcome in managing gingivitis. Therefore, the recommended guideline is to visit the dentist every six months.
Quit smoking
Active smoking causes dry mouth, bacterial accumulation, and reduced immunity. As a result, gingivitis is imminent. Nonetheless, averts the problem.
Eating a balanced diet.
Eating healthy prevents hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, and low immunity. As a result, the risk of developing gingivitis reduces.
Practising oral hygiene
Practices search as regular brushing of teeth, flossing, and use of mouth wash discourages the growth of bacteria that can contribute to gingivitis.
Therefore, observing good oral health practices will save you from gum inflammation.
In conclusion, take action hurriedly to resolve gingivitis before complications set in.
Featured Post
DL Mining Launches Ethereum Contract Participation Service, Helping Users Earn $2K Stable Daily Returns
Zizo Gala-Mkhize-
October 20, 2025
Soapie Teasers
Sister Sites
Most Popular
List of 6,000+ Dofollow Commentluv Blogs FREE (Updated 2025)
January 16, 2025
Five Do’s For a Healthy Turnover That Bolsters Talent-Retention
October 20, 2025
A Wood-Burning Stove in a Tent: A Guide to Safe Hot Tenting
April 08, 2021
Popular posts
Footer Menu Widget
Created By Blogspot Theme | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates

Social Plugin